FortiClient in the Security Fabric
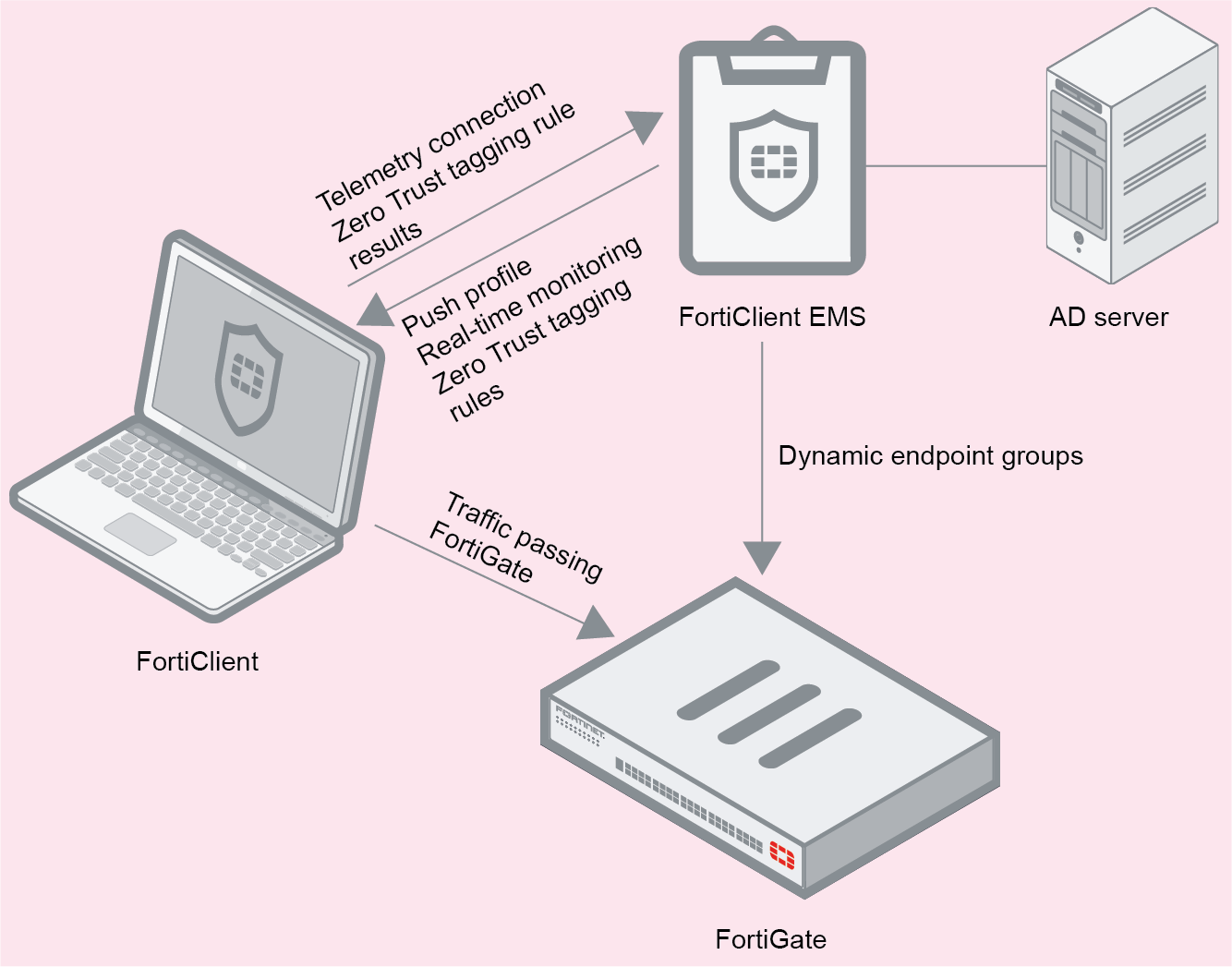
In this scenario, FortiClient Telemetry connects to EMS to receive a profile of configuration information as part of an endpoint policy. EMS is connected to the FortiGate to participate in the Security Fabric. EMS sends FortiClient endpoint information to the FortiGate. The FortiGate can also receive dynamic endpoint group lists from EMS and use them to build dynamic firewall policies. EMS sends group updates to FortiOS, and FortiOS uses the updates to adjust the policies based on those groups. This feature requires FortiOS 6.2.0 or a later version.
FortiClient 6.4 does not directly connect to FortiOS. FortiOS receives FortiClient data only from EMS.
|
|
FortiGate does not provide configuration information for FortiClient and the endpoint. An administrator must configure FortiClient using an EMS endpoint policy. |
Following is a summary of how the FortiClient Telemetry connection works in this scenario:
- EMS is connected to the FortiGate as a participant in the Security Fabric.
- FortiClient Telemetry attempts connection to EMS. Based on the EMS configuration, FortiClient may receive an SSL certificate from EMS to verify the connection. If the certificate is valid, FortiClient Telemetry connects to EMS.
- EMS sends the endpoint information received via FortiClient Telemetry to FortiOS.
- FortiClient receives a profile of configuration information from EMS as part of an endpoint policy.
- EMS sends Zero Trust tagging rules to the endpoint.
- FortiClient checks the endpoint using the provided Zero Trust tagging rules and sends the results to EMS.
- EMS receives the results from FortiClient and dynamically groups the endpoints according to the results.
- FortiOS pulls the dynamic endpoint group information from EMS. You can use this data to build dynamic firewall policies.
- EMS sends dynamic endpoint group updates to FortiOS. FortiOS uses the updates to adjust the policies based on those groups.
|
|
For details about configuring dynamic endpoint groups in FortiOS, see the FortiClient EMS Administration Guide. |
FortiClient follows the endpoint profile configuration that it receives from EMS. EMS locks FortiClient settings so that the endpoint user cannot manually change FortiClient configuration.
Only EMS can control the connection between FortiClient and EMS. You can only disconnect FortiClient from EMS.
The EMS server's IP addresses are embedded in FortiClient deployment packages created in EMS. This allows the endpoint to connect FortiClient Telemetry to the specified EMS server.
EMS sends the following endpoint information to FortiOS:
- User profile:
- Logged-in username
- Full name
- Email address
- Phone number
- User avatar
- Social network account IDs
- MAC address
- OS type
- OS version
- FortiClient version
- FortiClient UUID
EMS also sends the following endpoint information to FortiAnalyzer:
- Telemetry/system information
- User avatar
- Software inventory
- Processes
- Network statistics
FortiClient directly sends the following information to FortiAnalyzer:
- Logs
- Windows host events

