FortiManager performance and sizing in closed networks
Here you can find best practice information about sizing a FortiManager that is acting as a FortiGuard Distribution Server (FDS) in closed networks.
When operating in a closed network, FortiGate devices are not connected to the Internet. This is a protective measure that adds security, but it means that FortiGate devices cannot retrieve updates directly from FortiGuard. FortiGate devices can instead get the latest FortiGuard updates through an Internet connected FortiManager acting as a FDS. When FortiManager is acting is as a FDS, it will process the updates for AV/IPS, Web Filtering database, and license checks.
A closed network configuration with a FortiManager FDS can be set up in either a cascade or air-gapped mode.
Network design and process
In the examples below, the following scenario is used:
- 24 x FortiGate 1800F devices across four data centers.
- One FortiManager cluster per data center.
- FortiGates use FortiManagers as the FDS for AV/IPS, license checks, and the Web Filtering database.
Two network design modes are demonstrated:
Cascade mode
Design:
The following topology diagram demonstrates the network design using cascade mode where FortiManager-A is connected to the Internet, and FortiManager HA 1-4 are not connected to the Internet. The FortiManager HA 1-4 clusters override to use FortiManager-A as the FDS to download package and database updates, and provide update and rating services to FortiGate devices.
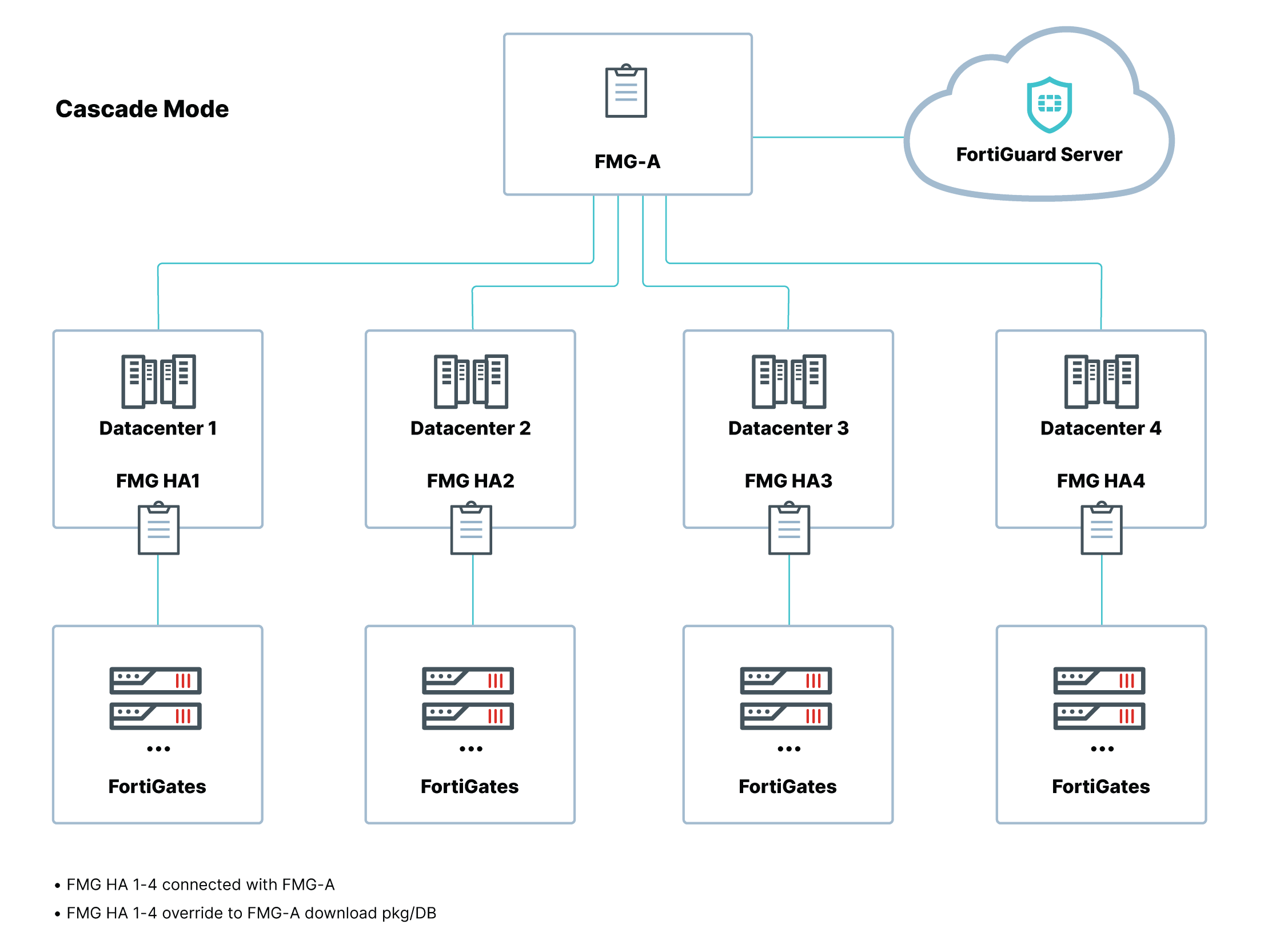
Process:
- FortiManager-A connects to the FDS to download AV/IPS packages, contracts, and Web Filtering database.
- FortiManager HA 1-4 have no Internet (FGD) access and override to use FortiManager-A to download the packages and database updates.
- FortiManager HA 1-4 provide update and rating services to the FortiGates.
Air gap mode
Design:
The following topology diagram demonstrates the network design using air-gap mode where there is no connection between FortiManager-A and the FortiManager HA 1-4 clusters. The FortiGuard update package must be imported on each FortiManager cluster using an internal-access only FTP server.

Process:
- In an air-gaped deployment mode, there is no connection between FortiManager-A and the FortiManager clusters.
- FortiManager-A downloads the updates from FortiGuard.
- FortiManager-A exports the downloaded packages.
- The FortiManager cluster imports the packages. This process must use an internal-access only FTP server.
Performance testing
|
|
The performance testing below was done using FortiManager and FortiOS devices running versions 7.0.0 or later. |
Web Filtering performance test case and results:
In a closed network, FortiManager will need to download the Web Filtering database and upgrade it in memory. The current Web Filtering database size is 7.5 GB, so the FortiManager will need (2 x 7.5 GB) + (8 GB) system memory, which is a minimum of 23 GB.
|
|
Some FortiManager units which do not meet the memory requirements, such as FortiManager 300E which includes 8GB of memory, cannot be used for this purpose. |
|
FortiManager Platform |
CPU |
Memory |
Cache |
CPU usage |
Max URL rating/s |
CPU |
Loss Rate <% |
|
FMG3900E |
24 |
128G |
7G |
70.00% |
90k |
64-bit |
0.0200 |
|
FMG3000F |
32 |
64G |
7G |
45.00% |
80k |
64-bit |
0.0200 |
|
FMG3700F |
40 |
386G |
7G |
72.00% |
90k |
64-bit |
0.023 |
|
FMG3000G |
32 |
128G |
7.3G |
74% |
90k |
64-bit |
0.01 |
AV/IPS performance test case and results:
FortiManager has no concurrent connection limitation, and the bottleneck for FortiGate updates from FortiManager is based on the available bandwidth for the network interface and the number of FDS workers configured to process download requests on the FortiManager.
The following scenarios demonstrate how various configurations of FDS workers and network ports affect the update time per FortiGate device as well as the FortiManager CPU usage.
|
|
The following performance testing was completed on a FortiManager-3000G with a 32-bit CPU, 128 GB of memory, and running version 7.0.2. |
|
|
The update package size used to calculate CPU usage below is based on the first time update to download the full AV/IPS package. |
Scenario 1
|
Number of FortiGates |
Update Time Per FortiGate |
FortiManager CPU Usage |
Network Bandwidth (port2 1Gbps) |
Max Concurrent Connections |
Update Package Size |
|
|
FortiGuard Update Service Daemon |
FDS Worker=1 |
|||||
|
1000 |
14 minutes |
< 1% |
98% |
960M |
1000 |
110M |
In the first scenario, there are 1000 FortiGate devices, one FDS worker is configured to process download requests on FortiManager, and port2 is used which supports speeds up to 1 Gbps. In this example, each FortiGate takes approximately 14 minutes to update, and the process uses 98% of the CPU on the FortiManager. With only one FDS worker and limited network bandwidth over port2, the AV/IPS update process becomes resource intensive on the FortiManager. Additional resources are recommended.
Scenario 2
|
Number of FortiGates |
Update Time Per FortiGate |
FortiManager CPU Usage |
Network Bandwidth (port4 25Gbps) |
Max Concurrent Connections |
Update Package Size |
|
|
FortiGuard Update Service Daemon |
FDS Worker=10 |
|||||
|
1000 |
4 - 20 seconds |
< 1% |
15% |
20G |
1000 |
110M |
In the second scenario, the number of supported FortiGates remain the same, but by changing the number of available FDS workers to 10 and using port4 which supports speeds up to 25 Gbps, each FortiGate is updated in only 4 to 20 seconds instead of 14 minutes, and the FortiManager CPU usage is 15% instead of 98%. The FortiManager in this scenario is suitably configured to support the AV/IPS updates for the number of FortiGates in the closed network.
By increasing the available FDS workers and choosing a network port that supports greater speeds, the load on the FortiManager CPU and the time to update each FortiGate is reduced.
Scenario 3
|
Number of FortiGates |
Update Time Per FortiGate |
FortiManager CPU Usage |
Network Bandwidth (port4 25Gbps) |
Max Concurrent Connections |
Update Package Size |
|
|
FortiGuard Update Service Daemon |
FDS Worker=10 |
|||||
|
3000 |
100 - 120 seconds |
< 10% |
50-95% |
20G |
3000 |
110M |
The third scenario uses the same port and number of FDS workers that are used in the second scenario but the number of FortiGate devices has been increased to 3000. The update time per FortiGate is increased to 100 - 120 seconds, and the FortiManager CPU usage is increased to between 50 and 95%.
As the number of supported FortiGate devices increases, the CPU usage and total time to update each FortiGate also increase.
To set the maximum number of FDS workers:
config fmupdate fds-setting
set max-work {1-32}
end
max-work = The maximum number of worker processing download requests (1 - 32, default = 1).
Conclusion
The following table provides recommendations about the FDS worker settings that should be configured based on the number of FortiGate devices in your environment. You can see the expected CPU usage and time to update each FortiGate device based on the recommended settings.
|
Number of FortiGate |
Recommended number of FDS workers |
CPU Usage |
Time to update all FortiGate devices |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 - 50 devices | Use default setting (1 FDS Worker) |
20 - 50% |
30 seconds |
| 50 - 1000 devices | Change max-worker to 10 | 50 - 90% |
1 minute |
| 1000 - 3000 devices | Change max-worker to 24 | 50 - 90% |
5 minutes |
|
3000 + devices |
Keep the max-worker set to 24. While you can configure the FDS worker setting up to 32, there is no benefit to CPU load beyond 24 in this scenario. |
- |
- |

