Managing a Compromised Hosts rescan policy
Compromised Hosts can be configured to scan previous entries on regular intervals or when a new package is received from FortiGuard so that FortiAnalyzer performs a rescan using the latest available definitions.
|
|
Requirements for managing a Compromised Hosts rescan policy:
|
When IOC rescan is performed, the Ioc_Rescan tag is added to rescanned logs. Event handlers which include the Ioc_Rescan tag in their filters will process rescanned logs and generate new alerts tagged with Ioc_Rescan. Real-time logs matching these event handler filters continue to generate alerts without the Ioc_Rescan tag.

By default, the following handlers include Ioc_Rescan tag for all filters:
- Default-Compromised Host-Detection-IOC-By-Endpoint
- Default-Compromised Host-Detection-IOC-By-Threat

To configure rescan settings and check rescan results:
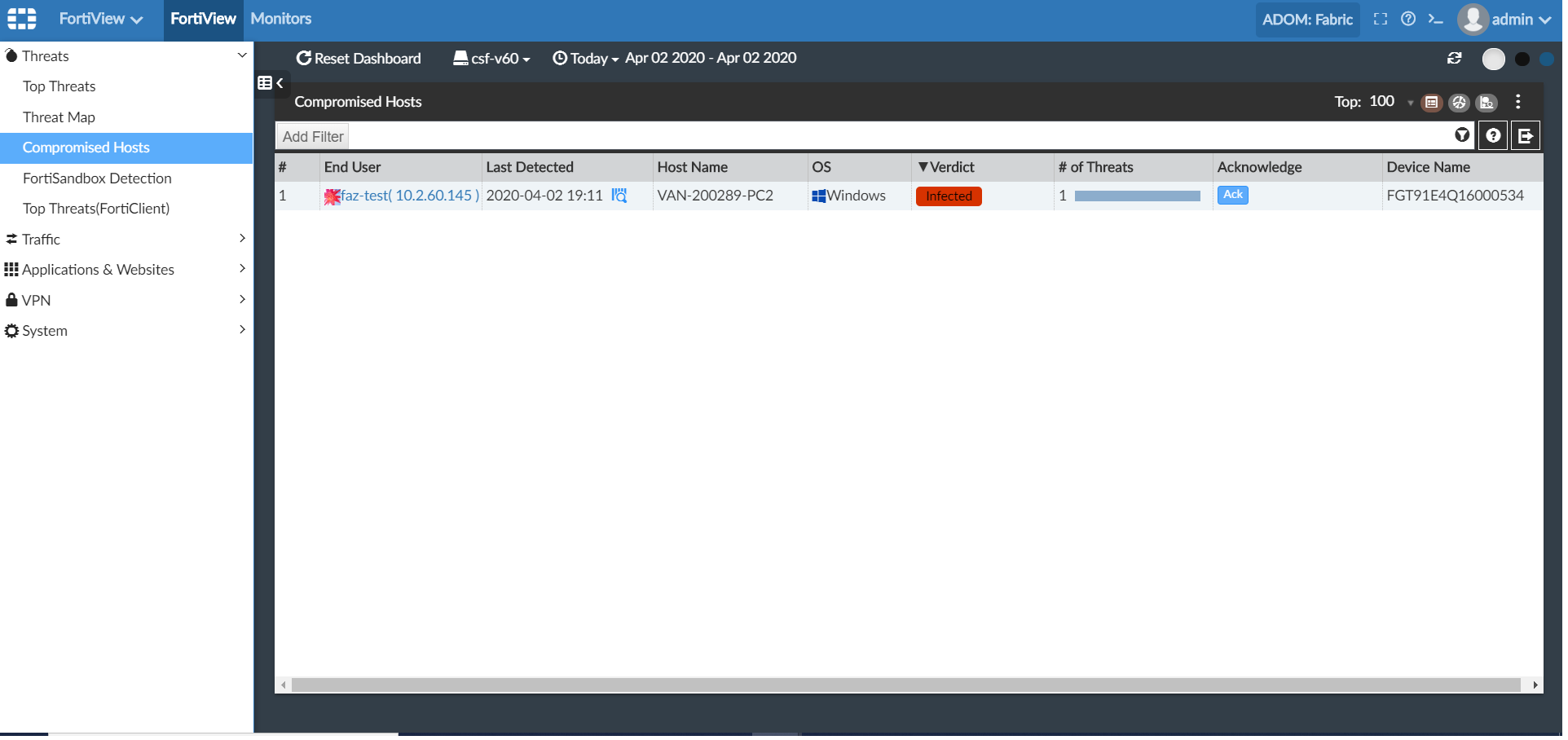
- Go to FortiView > FortiView > Threats > Compromised Hosts.
- Click the Compromised Hosts settings menu.
The Compromised Hosts settings window opens.
- Enable a global rescan policy.
- Under Compromised Hosts Rescan Global Settings, toggle Enable Global Compromised Hosts Rescan to the On position.
- Set the running time to a specific hour of the day, or select package update to perform a rescan when a package update is received.
- Enable policy settings for the current ADOM.
- Under Compromised Hosts Rescan Current ADOM Settings toggle Enable Current ADOM Compromised Hosts Rescan to the On position.
- Select the log types to be scanned (DNS, web filter, and/or traffic logs).
- Set the number of previous days' logs to be scanned.
By default, all log types are selected, and the scan will cover the last 14 days. The maximum recommended number of scan days is calculated based on historical scan speeds, or 30 days if no previous scans have been done.
- Rescan jobs are shown in the Rescan tasks table, which includes:
- Start Time: The task's start time.
- Status: The status of the task (complete, running, etc.).
- Percentage: Task progress as a percentage.
- End Time: The task's end time.
- Threat Count: The total number of logs with threats.
- Log Count: The number of logs included in the rescan.
- Package Update Time: The IOC package update time.
- Blacklist Count: A count of the newly detected threats added to the blacklist.

Running tasks can be canceled by clicking the cancel icon in the Status column.
- Select a non-zero threat count number in the table to drill-down to view specific task details, including the Detect Pattern, Threat Type, Threat Name, # of Events, and Endpoint.

Click the return icon to return to the settings window.
A rescan icon is displayed in the Last Detected column if threats are found during a rescan. To view only those hosts that had threats found during a rescan, select Only Show Rescan from the settings menu.