Securing OWA with FortiWeb
You can use FortiWeb’s site publishing features to authorize clients that want to connect to web applications such as Microsoft’s Outlook Web App (OWA).
This site publishing feature can replace the web publishing functionality provided by Microsoft’s Threat Management Gateway (TMG). FortiWeb also provides additional security features that protect the application after a successful login.
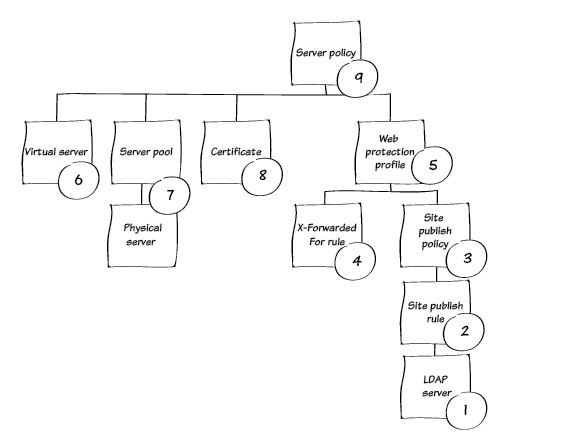
You create the FortiWeb configuration that publishes and protects web applications using a server policy.
A server policy is made up of several other configuration objects, including:
- Web protection profile — A set of security-related configuration objects.
- Virtual server — The IP address where FortiWeb receives client requests for access to the web application.
- Server pool — A backend server or servers where the web application is located.
- Certificate — Certificate to use for SSL encryption.
The numbers in the illustration correspond to the recipe instructions for the configuration objects.
This guide assumes that:
- Basic configuration is complete, including IP addresses, routing, and DNS information.
- The operating mode is reverse proxy (the destination for requests for the web application is a virtual server IP address on FortiWeb, not the back-end server where the application resides)

